This announcement of Eva Seydl, Program Manager at Microsoft, made my week! Start VM on Connect, a feature well known to most of the WVD rockstars as a solution to start virtual machines in Personal Host Pool scenarios is now also available for Pooled Host Pools.
In this blog you will learn, how to configure Start VM on Connect for Pooled Host Pools, Personal Host Pools and how to shut down VMs, when the users are logging off.
# Prerequisites
If you want to get started with Start VM on Connect in general you need to know a few things about it. It’s a feature that allows you to start virtual machines, but not yet to stop and deallocate them!
Additionally, it’s important to mention, that the feature supports ony the following Remote Desktop Clients:
The WVD web client: (https://rdweb.wvd.microsoft.com/arm/webclient) The Windows client (from version: 1.2748 or later) – Connect to Windows Virtual Desktop Windows 10 or 7 – Azure | Microsoft Docs Android client (from version 10.0.10 or later) – (https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.microsoft.rdc.androidx) macOS client (from version 10.6.4 or later) – (https://apps.apple.com/app/microsoft-remote-desktop/id1295203466?mt=12) The iOS client is currently NOT supported! Updates can happen at any time to change this.
To make the feature work in your environment, the second prerequisite is to create a custom role for Start VM on Connect. This can be achieved by granting access to the following set of permissions:
- Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines/start/action
- Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines/read
# How to create the custom role
First, you have to open your subscription from the Azure Portal. Click on Access control (IAM) to create a custom role.
In the top center of the screen click on “+Add” to create the new role and select “Add custom role”.
Now you have to give your role a name. I’ve chosen: “WVD Start VM on Connect”, which allows me to identify the role I need easily. Give your new role a description to understand easily, what this role is for, and click on Permissions.
Now click on “+Add permissions” and select the permissions you want to grant for this role. Like mentioned above you need:
- Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines/start/action
- Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines/read
Alternatively, import the following JSON file for your role:
| |
Now, click Review + create and confirm another time by clicking “create“.
Once the task is completed, you will get the following notification.
As the role is created, you need to assign this custom role to the WVD service. This can be achieved by clicking on “Role assignments” in your subscription, followed by clicking “+Add” > “Add role assignment“.
Now you just need to pick the recently created role, which is WVDStartVMOnConnect in my case, and assign access to Windows Virtual Desktop as a service. Once this is done, the role assignment completed successfully.
# Enable “Start VM on Connect for Pooled Host Pools“
On 12 May, Eva Seydl, Program Manager at Microsoft announced the availability of Start VM on Connect for Pooled Host Pools! This is awesome news, because it allows the first user connecting to a turned off Session Host to turn it on an allows an even more flexible way of scaling. Additionally, it allows you to scale down your Virtual Machines to ZERO, which is a huge cost saving opportunity for your environments.
The following describes the way to configure Start VM on Connect for Pooled Host Pools.
The important thing you need to know is, that this feature is currently in Preview. For that reason there is no graphical button to turn this feature on and it actually requires PowerShell.
Now log on to your Azure account with administrative privileges for WVD. Additionally make sure you have the Az.DesktopVirtualization module installed.
| |
Now you need to identify the Pooled Host Pools in your environment, you can achieve this by the following line of code:
| |
# Turn on the feature for a single pooled HostPool
| |
# Turn on the feature for ALL pooled HostPools
Information: Make sure you’re in the correct AZ Context in case you’re handling multiple subscriptions in your environment. Usage and more information can be found here: (https://web.archive.org/web/20230326143059/https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/powershell/module/az.accounts/set-azcontext?view=azps-5.9.0#syntax)
| |
# Turn off the feature for a single Pooled HostPool
| |
# Turn off the feature for all Pooled HostPools
| |
# Enable “Start VM on Connect for Personal Host Pools“
If you want to enable Start VM on Connect for Personal Host Pools, that’s also not a problem and can easily be achieved by using the Azure Portal. If you wish to do this by PowerShell, this can also be achieved and will be explained in the following subchapters.
# Enable the feature for a single Personal Host Pool (Azure Portal)
The easiest possibility of managing the Start VM on Connect feature is currently (last reviewed 18.05.2021) the Azure Portal. Where it’s not possible to achieve this for Pooled Host Pools, the Microsoft Product Group enabled this feature already for the Personal Host Pools.
All you need to do is to log into the Azure Portal using: https://portal.azure.com and navigate to the Windows Virtual Desktop Service. Arrived in the Host Pool overview, you will find the Pooled and Personal Host Pool types. We select the Personal Host Pool we want to enable to continue. Now we need to select Properties to find this option.
As a last step, you only need to enable the “Start VM on Connect” feature, while hitting Yes and clicking on “Save” in the upper corner. That’s it!
# Enable the feature for all Personal Host Pools (PowerShell)
If you want to enable the feature for all Personal Host Pools, we need to use the PowerShell again. Please use the following script to allow all Personal Host Pools for Start VM on Connect.
Information: Make sure you’re in the correct AZ Context in case you’re handling multiple subscriptions in your environment. Usage and more information can be found here: (https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/powershell/module/az.accounts/set-azcontext?view=azps-5.9.0#syntax)
| |
# Disable the feature for Personal Host Pools (Azure Portal)
Disabling the feature for a single Personal Host Pool, is as simple as enabling it. Just follow the steps from the previous subchapter and select “No” in the option field from within the Host Pool property page.
# Disable the feature for all Personal Host Pools (PowerShell)
If you want to disable the feature for all Personal Host Pools, please use the following script. Information: Make sure you’re in the correct AZ Context in case you’re handling multiple subscriptions in your environment. Usage and more information can be found here: (https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/powershell/module/az.accounts/set-azcontext?view=azps-5.9.0#syntax)
| |
# Enable “Shutdown virtual machines at LogOff“
A few weeks ago, Microsoft Global Black Belt Bernd Löhlein blogged about shutting down the Session Hosts and deallocating them, to not consume more money from your subscription, when the users log off. The solution is great for Personal Host Pools, but shouldn’t be used with Pooled Host Pools, as there might be more people working on the Session Host concurrently. Please find Bernd’s blog here: (https://techcommunity.microsoft.com/t5/windows-virtual-desktop/deallocate-vm-on-user-logoff/m-p/2280211)
# Shutting down Pooled Session Hosts
To achieve this we have two possibilities:
- Shutting down the virtual machines based on a time based metric
- Using the WVDLogix Autoscale Tool to scale down machines
To shut down the VMs based on a time based metric, we need to create an Automation Account in our subscription.
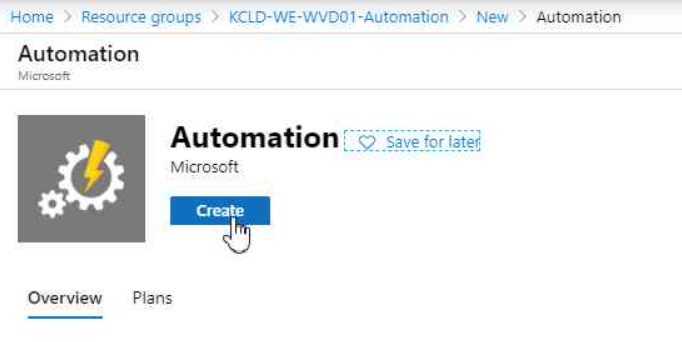
On the next page, we´ll give our Automation Account a name, select the subscription, the RG we´ve created, and the operating location, which is West Europe in my case. You also have the possibility to create a RunAs Account, which is not needed for the solution, which we´re going to provision right afterwards. Hit “Create” once you´re finished.
After a few seconds, our storage account is ready to be used and we can go to the resource, which presents us the basic overview of an Automation account.
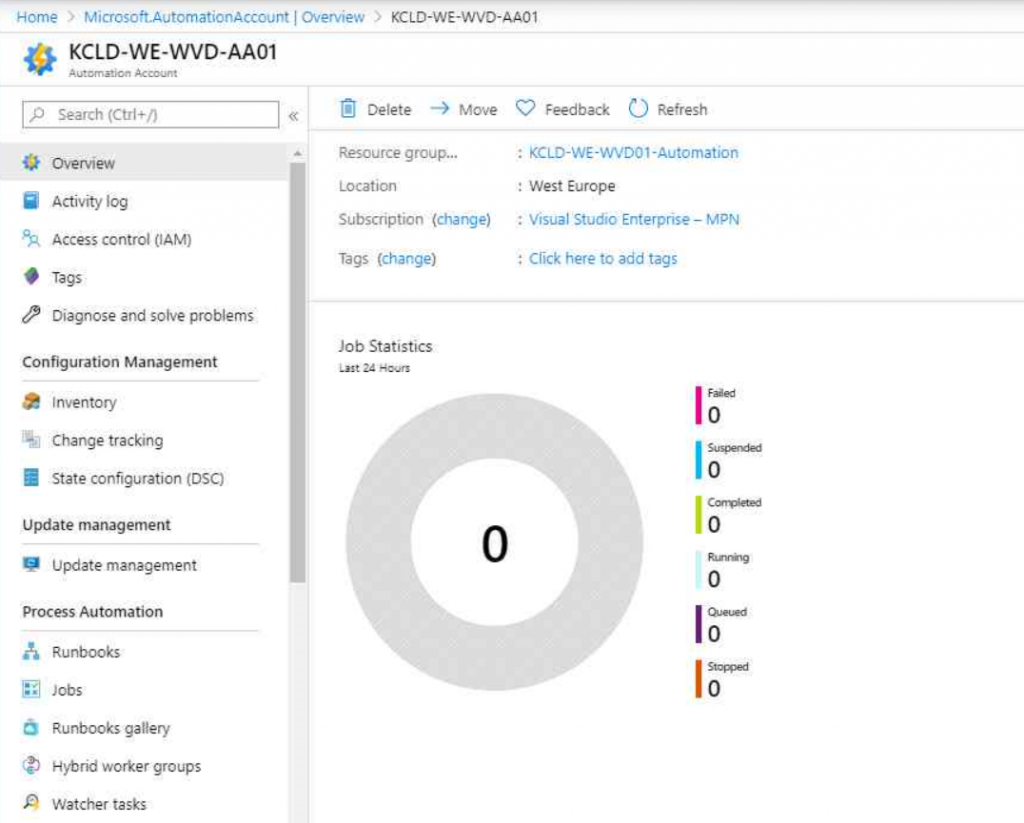
In here, we need to scroll down on the left hend side until we reach “Start/Stop VM”, which is the solution we want to install.
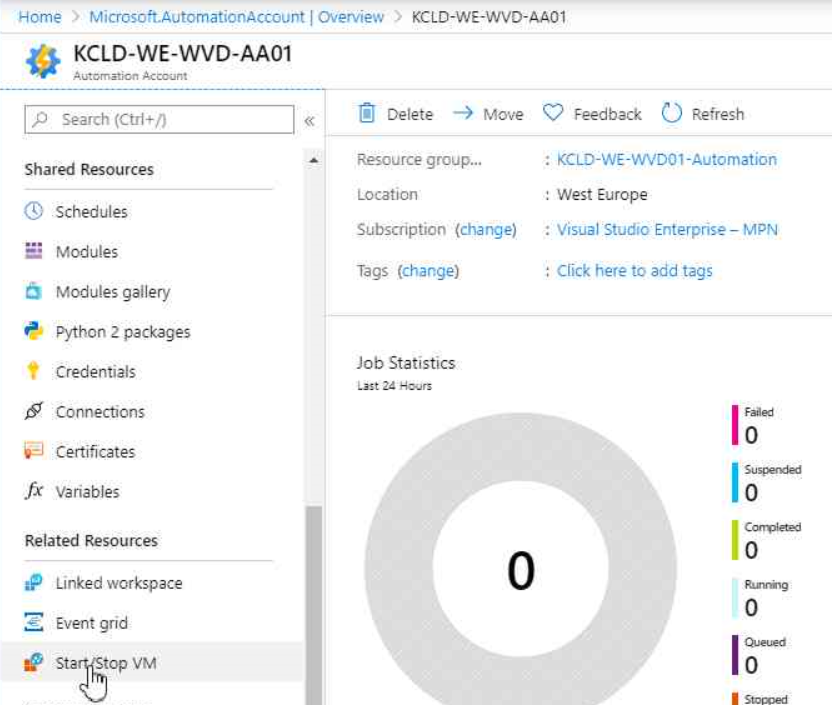
It´s obvious that we´re going to click on “Create”, but I´m very excited to see, what you´re saying about what this solution delivers additionally, when correctly configured. For now we click “Create” again to provision the solution.
The agent will guide us through the deployment of the solution, which requires the following components:
- Log Analytics Workspace (Can be created from within the solution deployment)
- Azure Automation Account (which has been created previously)
- Parameters
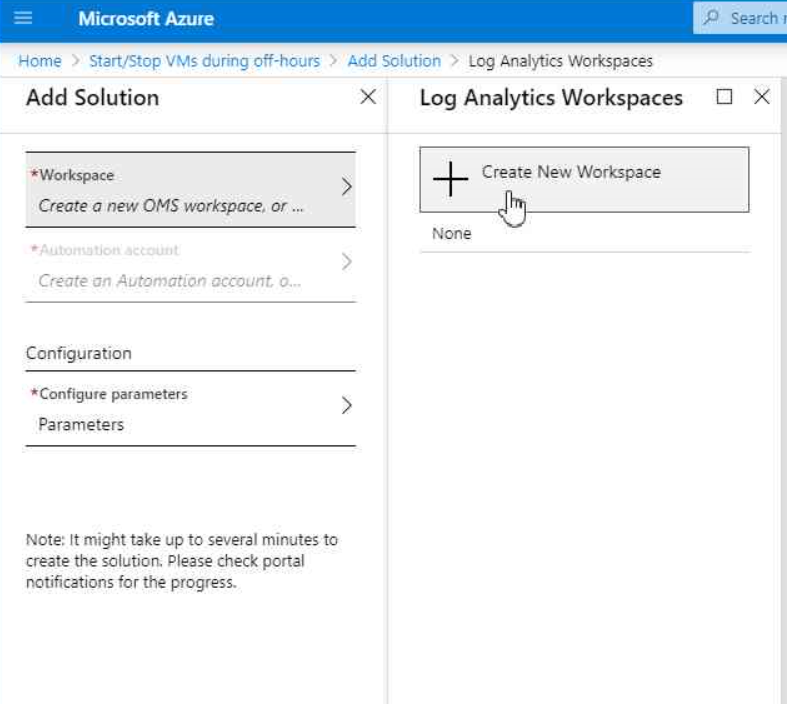
After you´ve created the Log Analytics Workspace and select the Automation Account created by us earlier, we leave the parameters empty for the moment. To not hide the possibilities from you, here is the screenshot of the initial configuration, to be defined from over here already.
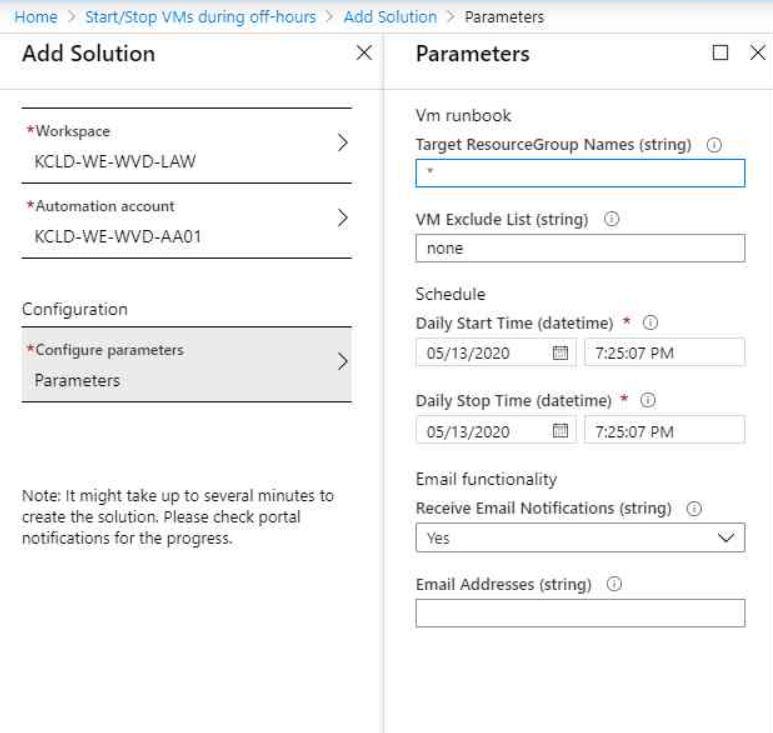
As mentioned before, we keep it empty and hit “OK” and click “Create”.
The deployment process is going to start and will finalize between 10-15 minutes and this will shutdown all machines, based on a time based metric automatically.
My personal recommendation is clearly to use the Autoscaling engine!
Thank you for reading this article!
Cheers, Patrick
